GitHub 101: The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide to Collaboration
Reading time: 10 minutes
This article aims to help students, web developers, and tech enthusiasts explore GitHub while I share tips from my journey as a small web agency and reinforce my own learning.
Introduction: What Is GitHub, and Why Should You Care?
GitHub is a valuable platform for anyone learning to code, working on software projects, or looking to build an online portfolio. It's where millions of developers save, track, and share their code, designed to make coding projects easy to manage. Think of GitHub as a digital binder that keeps all your files, projects, and code changes neatly organized and accessible whenever you need them. It’s especially popular because it allows multiple people to work on the same project at the same time without overwriting each other's work.
In this article, I'll walk you through GitHub's essential features, show you how to set up a project, and introduce some helpful commands and workflows.
1. A Quick History of GitHub
GitHub was founded in 2008 by four developers: Tom Preston-Werner, Chris Wanstrath, PJ Hyett, and Scott Chacon. They aimed to make it easier to track and manage changes in code, a practice called version control. In 2018, GitHub was acquired by Microsoft for $7.5 billion, showcasing its value in the tech world.
Fun Fact: GitHub is built on top of Git, a version control system created by Linus Torvalds, who also created the Linux operating system. Git’s design simplifies saving versions of your projects, making collaboration smoother and providing backup copies if things go wrong.
“GitHub is the home for all developers. By joining forces with Microsoft, we strengthen GitHub’s commitment to being an open platform and provide developers with even more resources to innovate.” - Satya Nadella, Microsoft CEO
2. Why Use GitHub? Key Benefits for Beginners and Pros
If you're new to coding, GitHub might seem intimidating, but it’s packed with features that make it useful for all skill levels. Here’s why GitHub is so popular:
- \*\*Version Control:\*\* Track changes to your code, making it easy to revert to previous versions if something goes wrong.
- \*\*Collaboration:\*\* Allows multiple people to work on the same project simultaneously without overwriting each other’s contributions.
- \*\*Portfolio Building:\*\* Show off your work! By hosting your projects on GitHub, you can build a portfolio that potential employers can view.
- \*\*Project Management:\*\* GitHub provides tools for managing your projects, including issue tracking and project boards.
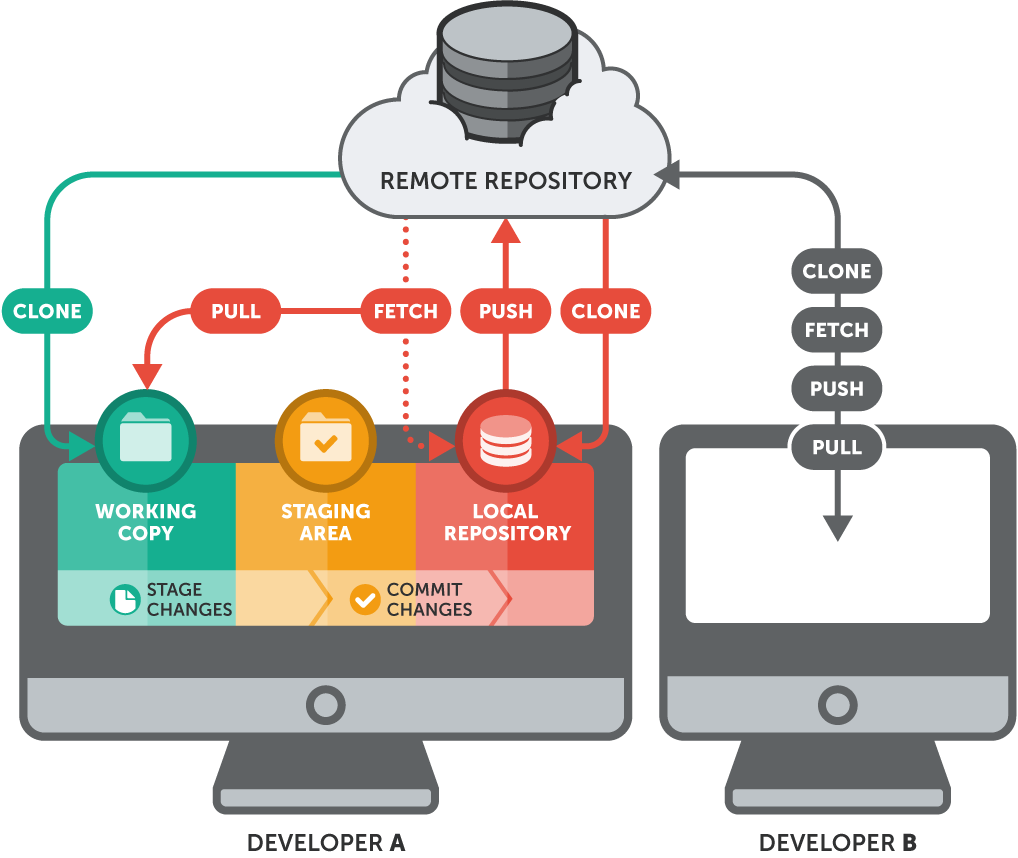
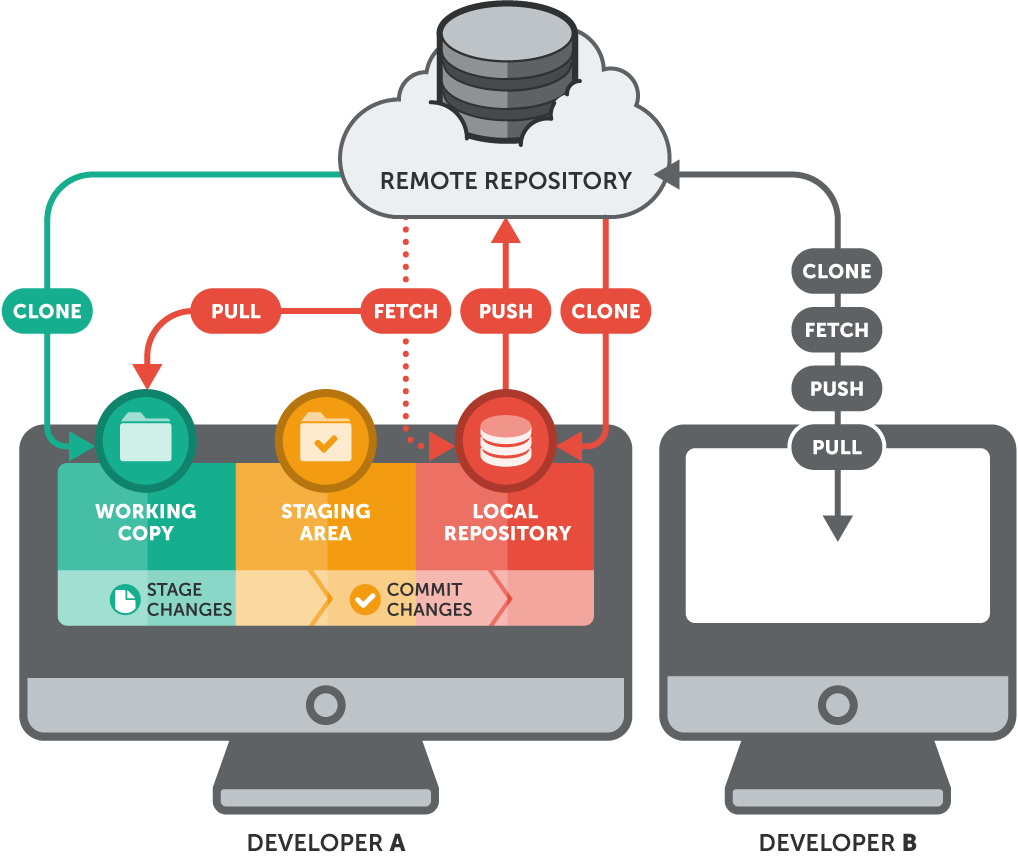
3. A Common GitHub Workflow: Your Step-by-Step Guide
Let’s walk through a basic workflow to help you understand how GitHub is used in day-to-day projects. This guide can be useful whether you're working alone or collaborating with a team.
Step 1: Create a GitHub Account
Head over to github.com and click on Sign Up to begin. Enter a unique username, your email address, and a secure password, then complete the CAPTCHA to verify you’re not a bot. After that, you’ll choose your plan — the Free plan is perfect to start with. Finally, check your email for a verification link, click it, and your GitHub account will be ready to use!
Step 2: Create a Repository
Start by creating a new repository on GitHub. Think of a repository as a project folder where all your files and code will be stored. Give it a descriptive name and choose whether it will be public (accessible to anyone) or private (only accessible to you and those you invite).
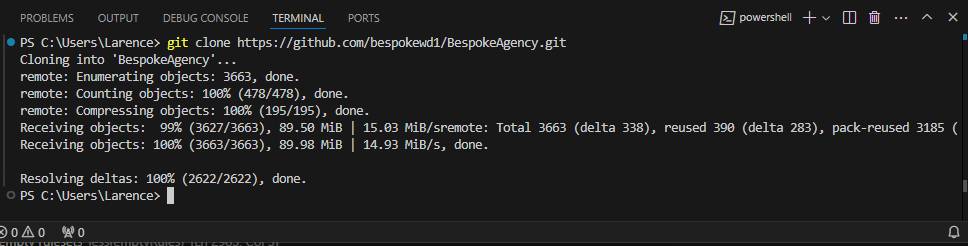
Step 3: Clone the Repository
To work on your code locally, you’ll need to clone (or download) the repository to your computer. This can be done using the command:
git clone [URL_of_your_repo]
Cloning creates a local copy of the repository, allowing you to make changes without affecting the original files until you’re ready.
Step 4: Create a Branch
To work on a new feature or fix a bug without affecting the main codebase, create a branch using the command:
git checkout -b [branch_name]
For example, if you’re adding a new feature, you might name your branch feature/add-login. This command does two things: it creates a new branch and switches you to that branch.
Benefits of Using Branches:
- Isolation: Allows you to work on different features or fixes in isolation from the main codebase, reducing the risk of introducing bugs.
- Collaboration: Multiple team members can work on separate branches simultaneously, making collaboration smoother and more organized.
- Clarity: Naming branches clearly (e.g., bugfix/login-error or feature/user-profile) helps everyone understand what changes are being made.
Step 5: Make Changes and Commit Them
Open your project in your code editor and start making changes. Once you’re happy with your progress, commit these changes to your local repository using:
git commit -m "Descriptive message about changes"
Make sure your commit message explains what changes you made; this helps others (and you) understand the project history.
Step 6: Push Changes to GitHub
To share your updates with others or save them on GitHub, use:
- git push origin [branch_name]
This uploads your commits from your local machine to the GitHub repository, making your changes visible to anyone who has access.
Step 7: Create a Pull Request (if collaborating)
When working on a team, you may create a new branch for your changes and open a Pull Request (PR) to merge those changes into the main project. A PR allows team members to review your code, discuss it, and suggest improvements before it’s integrated into the main project.
Step 8: Review and Merge Pull Requests
Once your changes are reviewed, they can be merged into the main branch. This is done by clicking the ‘Merge’ button on the PR page on GitHub. Merging integrates your changes with the main codebase, allowing others to use your work.
4. Other Version Control Systems: A Brief Overview
While this article focuses on GitHub, it’s important to know that there are other version control systems available, such as:
- Bitbucket: Similar to GitHub, but also supports Mercurial (another version control system). Bitbucket is often used in professional environments due to its strong integration with other Atlassian products like Jira.
- GitLab: Offers similar features as GitHub but includes built-in Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) capabilities. GitLab focuses on DevOps and automating the software development process.
In this article, we are focusing on GitHub because it’s user-friendly and widely adopted, making it the go-to choice for many developers. Its collaborative features and robust community support make it ideal for beginners and experienced developers alike.
5. Top Commonly Used Commands: Cheat Sheet for Developers
Understanding some basic Git commands will make your experience with GitHub much smoother. Here are some essential commands to get you started:
| Command | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| git clone \[URL] | Copies a repository from GitHub to your local machine | git clone https://github.com/user/repo.git |
| git status | Shows the current status of the repository | git status |
| git add \[file] | Stages a file for commit | git add index.html |
| git commit -m "message" | Commits the staged changes with a message | git commit -m "Add homepage layout" |
| git push origin \[branch_name] | Pushes your commits to the specified branch on GitHub | git push origin feature/add-login |
| git pull origin \[branch_name] | Fetches changes from the remote repository and merges them | git pull origin main |
Note: These commands can be executed in the terminal or command line interface. If you're using an IDE like Visual Studio Code (VS Code), it also has a user-friendly interface for Git operations, which we can explore in a future article.
6. Advanced Uses of GitHub
Once you’re comfortable with the basics, GitHub offers advanced features to enhance your workflow:
- Branch Protection Rules: Set rules to protect critical branches, ensuring that only approved changes can be merged.
- Continuous Integration (CI): Integrate with CI tools like GitHub Actions to automate testing and deployment of your code, ensuring high quality and efficiency.
- Forking Repositories: Create a copy of another user’s repository to experiment with changes without affecting the original project. This is particularly useful for contributing to open-source projects.
- Using Issues and Project Boards: Organize your work by creating issues for bugs or tasks and managing them with project boards, providing a clear overview of progress and priorities.
Here are some easy-to-use GitHub projects that beginners can practice and fork, along with their difficulty ratings and descriptions:
HTML5 Boilerplate (Difficulty: 1)
This project is a powerful front-end template that provides a solid foundation for building fast, robust web applications. It includes all the necessary elements to kickstart your development process, making it ideal for beginners. You can fork it at https://github.com/h5bp/html5-boilerplate.
Personal Portfolio Template (Difficulty: 2)
This customizable portfolio template is designed to showcase your work with a modern aesthetic using HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. It’s an excellent way to present your projects and skills to potential employers. You can find it and fork it at https://github.com/codewithsadee/vcard-personal-portfolio.
Bootstrap Templates (Difficulty: 2)
This repository offers a collection of responsive front-end templates built with Bootstrap, allowing you to create sleek, modern websites quickly. It's perfect for those looking to learn how to use Bootstrap effectively. You can explore and fork it at https://github.com/mdbootstrap/bootstrap-templates.
Super Mario Bros. in JavaScript (Difficulty: 3)
This project features a fully playable version of Super Mario Bros. built with JavaScript. You can fork this repository to understand the game mechanics, modify the code, and even create your own levels. It’s a fun way to enhance your JavaScript skills while working on an interactive project. You can fork it at https://github.com/meth-meth-method/super-mario.
These projects provide a fantastic opportunity to enhance your coding skills, explore GitHub, and gain hands-on experience with real-world applications. By forking these repositories, you can modify the code and personalize them to improve your understanding and expertise in web development. Happy coding!
Conclusion
Getting started with GitHub might seem overwhelming at first, but once you familiarize yourself with the basic commands and workflows, you'll find it an invaluable tool in your web development toolkit. Whether you’re working on personal projects or collaborating with a team, GitHub simplifies the coding process and helps you stay organized.
Remember, practice is key! Explore the sample repositories, play around with the commands, and soon you’ll feel right at home on GitHub. Happy coding!
Image Credits: Images are used for illustrative purposes only. All rights to respective owners.
This blog was created to share knowledge and foster a community of learners.